In a series of blogs over the next several months, we will look at a broad range of subjects to show how the proposed National Museum of the American People compares to and diverges from our nation’s two best story-telling museums, the US Holocaust Memorial Museum and the National Museum of African American History and Culture. This blog simply lists the topics that will be discussed in future blogs. Topics will include:
- The feasibility studies that led to creation of the USHMM and the NMAAHC and how the NMAP will follow the lead of the African American feasibility study.
- How both museums tell their stories and how the NMAP will follow their examples.
- An exploration of the timeline to build both museums and why the NMAP will aim to follow the USHMM lead in this area.
- The USHMM is independent of the Smithsonian Institution; the NMAAHC is a part of the Smithsonian. This blog will discuss the governance structure that might work best for the NMAP.
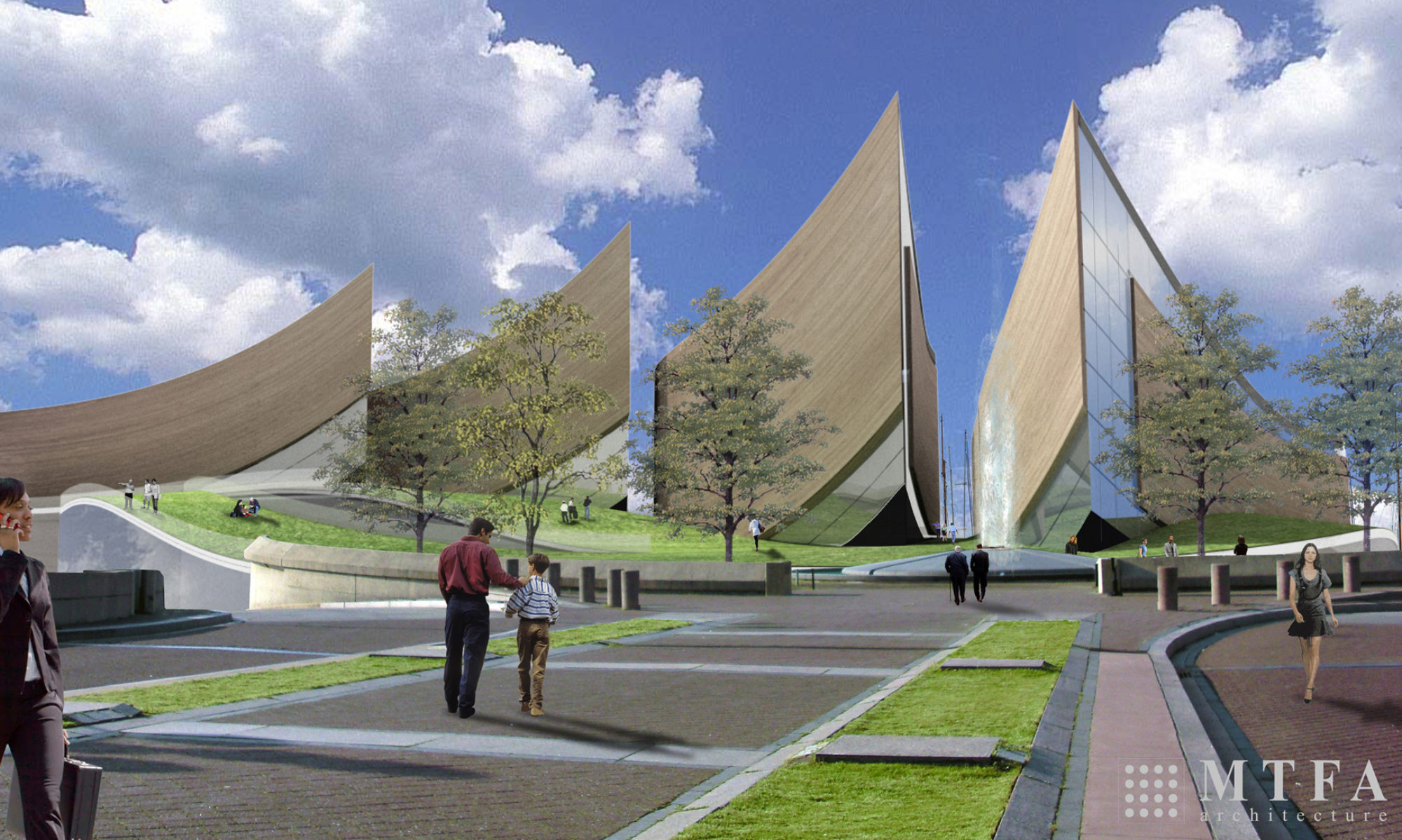
- Both the NMAAHC and the USHMM have notable buildings in which they are housed and a local architecture firm (MTFA) has developed a rendering of what the NMAP could look like (see photos above). The role of the architect for these museums and how the building design relates to their stories will be discussed.
- As story-telling museums, the visitor at both existing museums are on a chronological path telling a dramatic story about significant historic events with a beginning, a middle and an end. Both museums employed the same exhibition designer. This blog will examine how both museums will inform how the NMAP tells its story.
- The USHMM and the NMAAHC used two different models to raise money to plan and build those museums. The NMAP plans to follow the lead of the USHMM to plan and build the museum.
- Both existing museums receive significant annual federal appropriations to operate their institutions. The NMAP plans to follow a different path without federal appropriations to operate the museum.
- This blog will explore the importance of location and a prime location being sought for the NMAP. The USHMM and the NMAAHC are both located In Washington between 14th and 15th Streets (renamed Raoul Wallenberg Place on the Holocaust Museum block). The African American Museum is on the north side of the National Mall and the Holocaust Museum is just to the south of the Mall, both prime locations.
- We will explore the visitor experiences at the NMAAHC and the USHMM and examine what that experience will be like at the NMAP.
- This issue will discuss the purpose of both existing museums and how they achieve it and will discuss the purpose of the NMAP and the plan to meet its purpose.
- The USHMM and the NMAAHC deal with the historic and contemporary ravages of genocide, racism, xenophobia, slavery and anti-Semitism. So will the NMAP.
- The USHMM has a scholarly Center for Advanced Holocaust Studies. The NMAP will have a Center for the Advanced Study of the American People with connections to scholarly institutions throughout the nation and the world.
- Both the USHMM and the NMAAHC welcome school groups and provide curricula material focused on their respective subjects. The NMAP will have a vigorous program to welcome students on their visits to Washington and plans to have a national outreach program to help teach civics that incorporates the history of every group that has come to this nation from the first to the present no matter where on Earth they or their ancestors came from.
- How much do visitors to the USHMM and the NMAAHC see their own stories told in those museums? The NMAP will tell the story of every American group and visitors from every country will learn about peoples from their nations who became Americans.
- The African American Museum’s story starts in Africa and in Europe and then quickly transfers to the New World and the United States. The Holocaust story focuses on the nation’s where the Holocaust was perpetrated and brings in the United States along the way and finishes with the two nations where most Holocaust survivors settled, Israel and the U.S. That museum has relations with nations throughout Europe. The NMAP will have relationships with nations throughout the world with countries that fed people into our nation over the eons and centuries through today.
- Both the NMAAHC and the USHMM have had strong bipartisan support in Congress and the White House. The NMAP will endeavor to have bipartisan support from all of our nation’s political leaders.
- How do all three museums compare with the National Museum of American History?
- How do they compare with the National Museum of the American Indian?
- How do they compare with the proposed National Museum of the American Woman?
- There are proposed national museums for Asian Pacific, Irish and Latino Americans. How would they fit in with the NMAP?
Sam Eskenazi, Director, Coalition for the National Museum of the American People







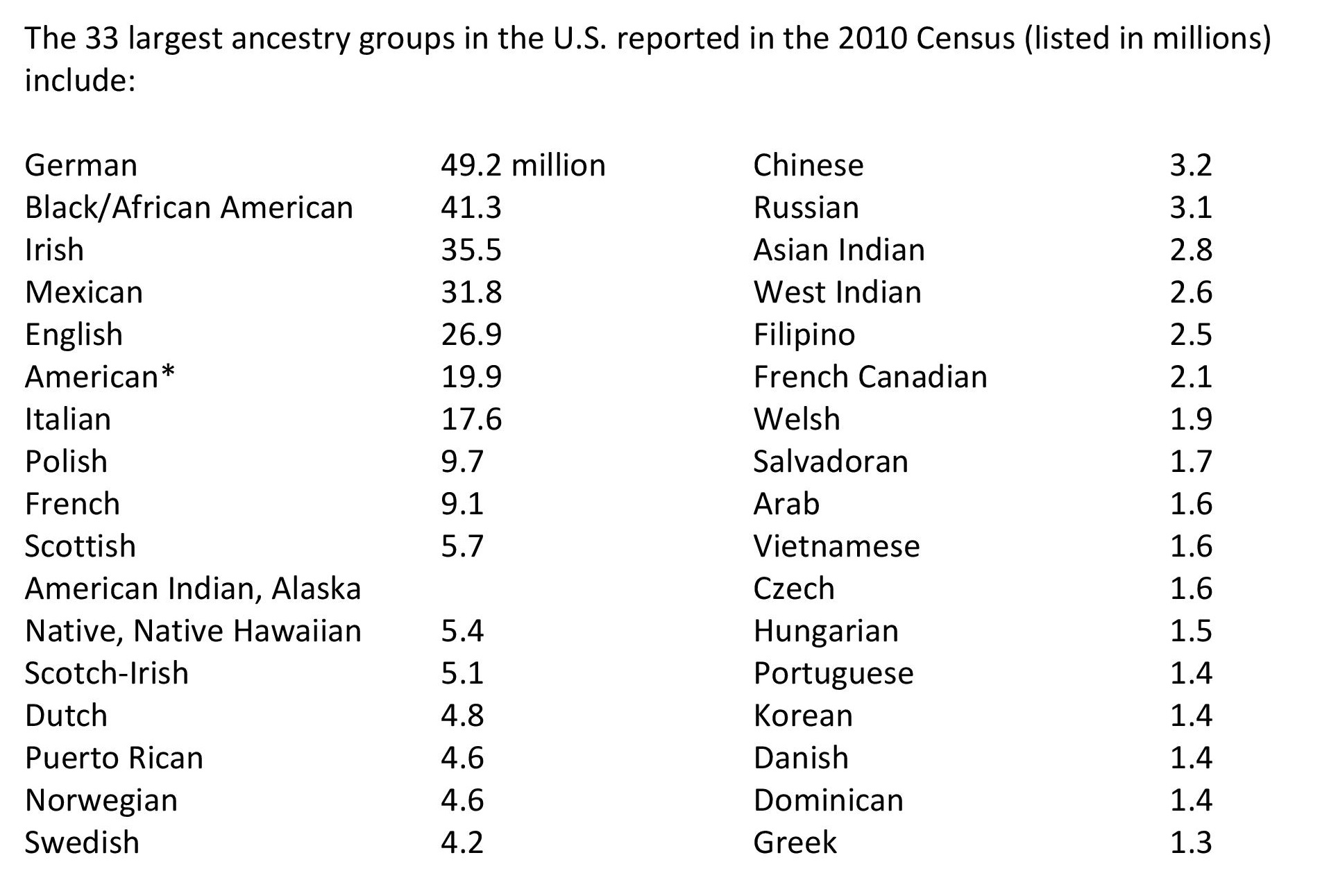 * Generally, people who put down “American” on the Census form have ancestors who came from England, Scotland, Ireland and Germany during the 17 and 18th centuries. They and their descendants thoroughly intermingled and 200 years later they describe their ethnicity as American.
* Generally, people who put down “American” on the Census form have ancestors who came from England, Scotland, Ireland and Germany during the 17 and 18th centuries. They and their descendants thoroughly intermingled and 200 years later they describe their ethnicity as American.





